If you’ve ever wondered about harmonics in audio, then you’ve come to the right place. We’ll dive into the fascinating world of harmonics, exploring how they affect sound quality, music production, and audio engineering. We’ll also help you understand the science behind them, from harmonic frequencies and distortion to overtones and waveform analysis. So let’s strike a chord and get harmonic because understanding harmonics in audio is music to our ears!
What are harmonics in audio? Harmonics are the higher frequency components of a sound that occur in integer multiples of the fundamental frequency, enriching the overall sound quality and character.
What are harmonics?
Harmonics refers to sound waves that are related to a fundamental frequency or pitch as integer multiples. The fundamental pitch is the lowest frequency that can be produced from a sound. In music, harmonics are used on string and wind instruments to produce sound, particularly for playing higher notes and obtaining notes with a unique tone color.

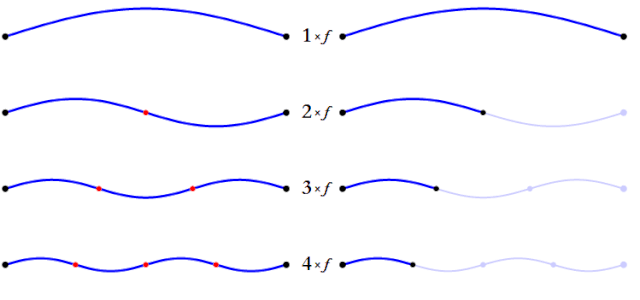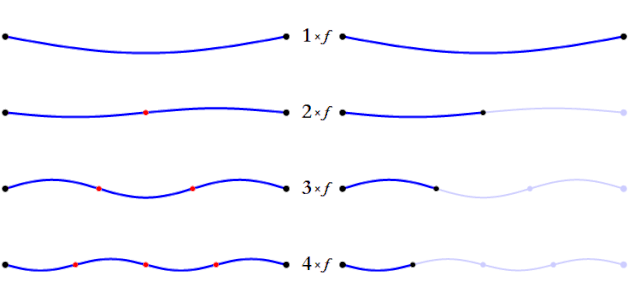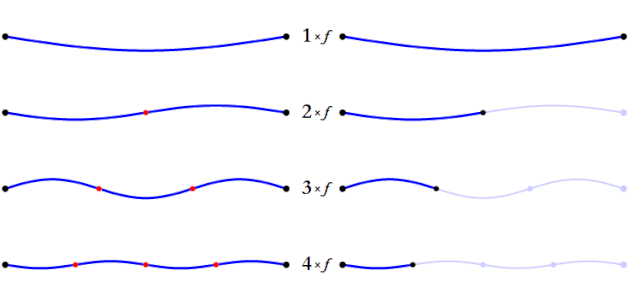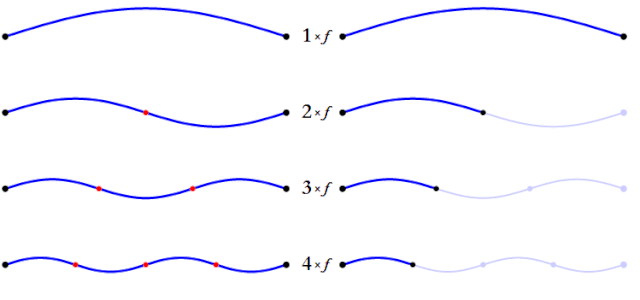
The balance of the harmonic overtones of the note you play depends on the instrument and the way you play it, affecting the distribution and balance of the partials or harmonic overtones of the sound. These harmonic overtones are responsible for allowing us to recognize different sounds and instruments, even when they are playing the same note.
AKAI Professional MPK Mini MK3

AKAI Professional MPK Mini MK3
The relationship between harmonics and timbre lies in the fact that the harmonic content of a sound determines its unique timbre, allowing our ears to distinguish between different instruments playing at the same pitch and loudness.
The timbre of an instrument is influenced by the relative strengths of the harmonics in each note. Adding harmonics to a tone gives it a richer timbre, making it more distinctive and recognizable.
Theories, such as Helmhotz’s proposition, suggest that the timbre of a sound affects consonance and dissonance through the interaction of the individual partials (harmonics) of notes, with beat frequencies between these partials causing dissonance, and the coincidence of partials resulting in consonance.
How to use harmonics in your music
To use harmonics in your music, you can employ the following techniques:
1. Sound design
Understand that harmonics are the foundation of the timbre of all sounds. Utilize this knowledge for sound design by using your DAW’s built-in EQ to boost the fundamental frequency or cut higher harmonics to make an instrument sound more ‘sine-like.’
Use planing to create solo lines, where chords become the melody. Experiment with the rhythm and the shape of the line to make your solo more interesting.
2. Prolong harmonic functions
Incorporate other chords from the same family to prolong the harmonic functions, reinforcing the tonal center. For example, you can play an I – vi – V – I progression instead of an I – V – I, where adding the vi prolongs the tonic function.
3. Harmonic planing
Use planing to create solo lines, where chords become the melody. Experiment with the rhythm and the shape of the line to make your solo more interesting. This technique can involve both diatonic and chromatic planning.
4. Harmonic analysis
Write Roman numerals underneath the chords of your favorite songs to understand their harmonic relationships. This process, called harmonic analysis, can help you see the relationships between chords and inspire your own compositions.
5. Harmonic distortion
Introduce harmonic distortion to add new harmonics that are musically related to the input signal. This can change the character and timbre of the sound, often resulting in a richer and more charismatic tone.
If you want even more tips and insights, watch this video called “I Make a Song With Only Harmonics” from the Ichika Nito YouTube channel.
Frequently asked questions (FAQ)
Do you still have questions about harmonics? Below are some of the most commonly asked questions.
What is the definition of harmonics in audio?
Harmonics in audio refers to frequencies that are integer multiples of a fundamental frequency. They play a crucial role in determining the timbre and overall sound quality of a musical note or instrument.
How do harmonics affect the timbre of an instrument?
Harmonics influence the timbre of an instrument by determining the blend of frequencies present in a sound. The presence, absence, or relative strength of specific harmonics creates the distinct character and tone of each instrument, allowing us to differentiate between them even when playing the same note.
Are all harmonics present in every musical instrument or sound?
Not all harmonics are present in every musical instrument or sound. The specific set of harmonics and their relative strengths vary depending on the instrument, the way it is played, and the individual characteristics of each sound source. This unique combination of harmonics is what gives each instrument its distinct timbre.
Conclusion
Well, folks, we’ve struck a chord with harmonics in audio! Now you’re ready to face the music and explore the world of harmonics and how they influence the sounds we create and enjoy. So, do you feel more in tune with harmonics now? And did I cover everything you wanted to know? Let me know in the comments section below (I read and reply to every comment).
If you found this article helpful, share it with a friend, and check out my full blog for more tips and tricks on audio production and music theory. Thanks for reading, and may your harmonics always be harmonious!
Key takeaways
This article covered harmonics in audio. Here are some key takeaways:
- Harmonics are frequencies that are whole-number multiples of a fundamental frequency.
- They are responsible for the unique timbre of different sounds and instruments.
- The relationship between harmonics and timbre is crucial in understanding how different sounds are perceived.
- Harmonics can be used creatively in music production to shape the tonal quality and character of a sound.
- Understanding harmonics can help producers and musicians make more informed decisions about their sound design and music creation processes.















