Welcome, fellow audiophiles, to another exploration of all things audio! In this blog post, we’ll explore bit depth in digital audio and equip you with the tools to understand its impact on audio quality, resolution, and more.
If you’re passionate about audio quality and eager to understand the intricacies of this fundamental concept, then you’re in for a treat! So are you ready to level up your audio game? Let’s dive in!
What is bit depth in digital audio? Bit depth in digital audio refers to the number of bits used to represent the amplitude of an audio signal. It determines the dynamic range and resolution of audio, with higher bit depths allowing for greater precision and detail in audio recordings. Understanding bit depth is essential for achieving optimal audio quality and ensuring an accurate representation of audio signals in the digital realm.
What is audio bit depth?
Audio bit depth refers to the number of bits used to represent the amplitude of an audio signal in digital audio recordings. It directly corresponds to the resolution of each sample, with higher bit depths indicating more detailed sound recordings. The table below summarizes the most common audio bit depths and their possible values.

| Audio Bit Depth | Number of Possible Values | Commonly Used In |
|---|---|---|
| 16-bit | 65,536 | Compact Disc Digital Audio (CD), DVD |
24-bit | 16,777,216 | DVD-Audio, Blu-ray Disc, Recording and bouncing audio, DVD |
| 32-bit | 4,294,967,296 | Professional audio production and mastering |
A 16-bit audio bit depth provides each sample with 65,536 possible amplitude values, which allows for a dynamic range of 96 dB. This is the standard bit depth used in Compact Disc Digital Audio (CD-DA).
A 24-bit audio bit depth provides each sample with 16,777,216 possible amplitude values, which allows for a much higher dynamic range of 144dB. This higher bit depth is commonly used in professional audio recording and production, as it allows for a more accurate representation of audio signals and reduced quantization noise.
A 32-bit audio bit depth provides an even higher resolution, with 4,294,967,296 possible amplitude values per sample. However, 32-bit audio is less common and typically used in specialized applications where extremely high audio resolution is required.
AKAI Professional MPK Mini MK3

AKAI Professional MPK Mini MK3
What should my sample rate and bit depth be?
The best bit depth for a sample rate depends on the application and the desired audio quality. For most music applications, a bit depth of 16 bits is considered standard and commonly used, especially when paired with a sample rate of 44.1 kHz. This is because 16 bits are sufficient to reproduce the audible frequency and dynamic range for the average listener, and 44.1 kHz is the standard sample rate for audio CDs.
However, for professional audio work or high-resolution audio production, a higher bit depth of 24 bits may be preferred for greater accuracy and audio quality during the mixing and mastering processes.
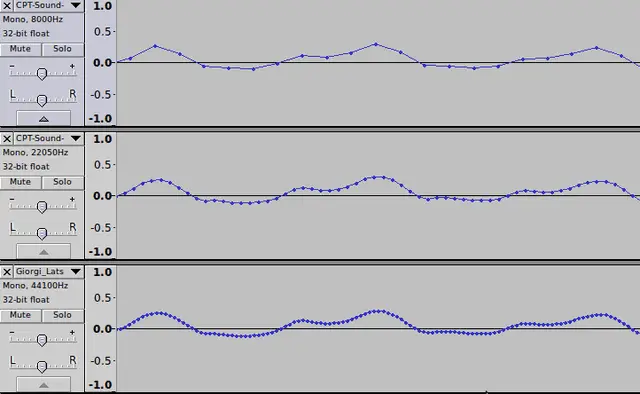
It’s worth noting that there are no strict limits to sample rate and bit depth, and higher values may offer advantages in certain scenarios. For example, a sample rate of 48 kHz is commonly used when creating music or audio for video production. Sample rates of 192 kHz with 24-bit depth are considered the gold standard for hi-res audio, although their practical benefits may be subjective and depend on individual preferences and requirements.
How does bit depth affect sound quality?
In practical terms, higher bit depths allow for a wider dynamic range, which is the difference between the quietest and loudest sounds that can be accurately captured in a digital recording. A larger dynamic range can result in more accurate and detailed audio recordings, particularly for music or other audio content with a wide range of volume levels.
…a bit depth higher than 16 bits may not necessarily result in a perceptible improvement in sound quality for most listeners…
For example, a bit depth of 16 allows for 65,536 possible amplitude levels, while a bit depth of 24 allows for 16,777,216 possible amplitude levels. This increased resolution can capture subtle nuances in audio, resulting in more accurate and higher-fidelity sound reproduction.
It’s important to note that the human ear has a limited dynamic range of sensitivity, typically ranging from 0dB (silence) to about 120dB (painfully loud sound). This means that a bit depth higher than 16 bits may not necessarily result in a perceptible improvement in sound quality for most listeners, as the dynamic range of the human ear is close to 20 bits.
What is the difference between bit depth and bit rate?
Bit depth and bit rate are two related but distinct concepts in digital audio and video. Bit depth refers to the number of bits used to represent the amplitude of each sample in a digital audio or video signal, while bit rate refers to the amount of data transmitted or processed per unit of time, typically measured in bits per second (bps).
Higher bit depths allow for a more accurate and detailed representation of the signal, while higher bit rates generally result in higher-quality audio or video with more data being transmitted or processed per unit of time.
If you want even more tips and insights, watch this video called “The Truth About Bit-Depth and Digital Audio Resolution” from the Production Advice YouTube channel.
Conclusion
And there you have it, folks! We’ve delved into the world of bit depth in digital audio and uncovered its importance in achieving optimal audio quality. From the basics of what bit depth is to its impact on audio resolution and fidelity, we’ve covered it all. So, did I answer your burning questions about bit depth? Let me know in the comments section below. I read and reply to every comment.
If you found this article helpful, don’t keep it to yourself; share it with a fellow audiophile. And be sure to check out our full blog for more tips and tricks on mastering the art of digital audio. Thanks for tuning in, and keep groovin’ to your favorite tunes.
Key takeaways
This article covered audio bit depth. Here are some key takeaways:
- Bit depth in digital audio refers to the number of bits used to represent the amplitude of an audio signal.
- Higher bit depths result in higher audio quality and greater detail in recordings.
- Bit depth impacts the dynamic range and resolution of audio, with higher bit depths allowing for wider dynamic range and greater resolution.
- Lower bit depths can result in quantization noise and loss of audio fidelity.
- Understanding bit depth is crucial for achieving optimal audio quality in digital audio recordings.
















Thank you for the information. I really appreciate it.