Picture this: you’re chillin’ in your studio, laying down some sick beats, and suddenly you realize the sound is all wonky. Maybe it’s too quiet, or there’s this annoying hiss that just won’t quit. You’re stumped, scratching your head, wondering how to fix it. And then it hits you: it has something to do with the line level. So, what exactly is line level in audio?
What is the line level in audio? Line level is the standard voltage level at which audio signals are transmitted between various pieces of audio equipment, such as mixers, amplifiers, and recording devices.
What is line level?
Line level is the voltage standard for audio signals that flow between your audio gear, like mixers, audio interfaces, and synthesizers. It’s a relatively high-level signal that drives a line input, as opposed to a lower-level microphone or instrument signal. There are two main line levels:

- Consumer line level (-10 dBV): Commonly used in consumer audio devices like home theater systems, PCs, and smartphones.
- Professional line level (+4 dBu): Used in pro audio equipment like studio mixers, audio interfaces, and outboard gear.
Imagine you’re recording a podcast and have a professional audio interface connected to your computer. Your computer sends audio at a consumer line level, while your interface expects a professional line level. This mismatch can cause all sorts of audio mayhem. To avoid this chaotic audio landscape, it’s crucial to understand line level and make sure you’re using the right gear for the job.
AKAI Professional MPK Mini MK3

AKAI Professional MPK Mini MK3
A beginner’s encounter with line level
Picture me, a newbie music producer just starting out in the audio world. One day, I was trying to record some fresh beats and noticed that the sound was super quiet, even with the volume cranked up. I couldn’t figure out what was wrong until a more experienced producer buddy of mine enlightened me about line level.
Turns out, I was using an audio interface with a professional line level while my keyboard was sending a consumer line level signal. Once I got the right gear and matched my line levels, my audio was crisp, clear, and loud enough to impress even the most discerning listeners.
Why is understanding line level important?
You might be wondering, “Why should I care about line level as a music producer or audio engineer?” Well, mastering line level is key to achieving high-quality sound in your recordings and live performances. It ensures that your audio gear plays well together and avoids any unwanted noise or distortion.
For instance, let’s say you’re recording a vocalist with a condenser microphone. You connect the mic to a preamp, which amplifies the mic’s weak signal to line level. From there, you send the signal to an audio interface or mixer, which expects a specific line level to work optimally.
If the preamp doesn’t provide the right line level, you could end up with a distorted or weak recording. That’s definitely not what you want when you’re striving for audio perfection!
How do you identify different types of line level signals?
Alright, so now that you know why line level is essential, let’s talk about how to identify different types of line level signals. Being able to recognize various line level signals will help you set up your gear correctly and avoid those pesky audio issues we talked about earlier.
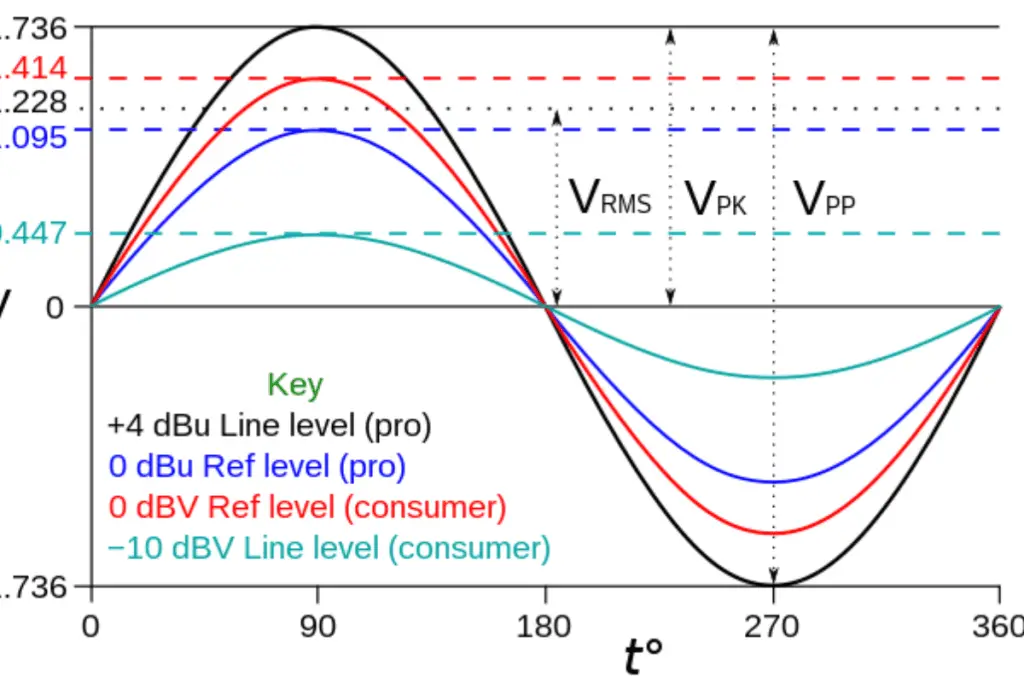
Here are some tips to help you identify different line-level signals:
- Check the specs: When in doubt, consult your gear’s user manual or spec sheet to find the line-level standard it uses. You can typically find this info online if you don’t have a physical copy.
- Look for labels: Many audio devices have labels near the input and output jacks that indicate their line level standard, like “-10 dBV” for consumer line level or “+4 dBu” for professional line level.
- Know your connectors: While not foolproof, certain connectors are more common with specific line level standards. For example, RCA connectors are often associated with the consumer line level, while XLR and 1/4-inch TRS connectors are more commonly used with the professional line level.
What are the common line level connectors and their uses?
So, you’ve got the lowdown on line-level signals, but what about the connectors? Let’s dive into some of the most common connectors you’ll encounter:
- RCA connectors: Also known as “phono connectors,” these guys are typically found in consumer audio gear. They’re often used for connecting home theater systems, DJ mixers, and other consumer-level devices.
- 1/4-inch TRS connectors: TRS stands for “Tip, Ring, Sleeve,” and these connectors are commonly used in professional audio equipment. They’re versatile, as they can carry both balanced and unbalanced signals. You’ll see them on mixers, audio interfaces, and even some keyboards and synthesizers.
- XLR connectors: These are the big guns of the audio world, with three pins and a locking mechanism. XLR connectors are used for balanced audio signals in professional gear, like microphones, preamps, and mixers. They’re known for their durability and resistance to interference.
If you want even more tips and insights, watch this video called “What is “Line Level”?” from the AVGenius YouTube channel.
Frequently asked questions (FAQ)
Do you still have questions about line level in the audio? Below are some of the most commonly asked questions.
What are the consequences of using mismatched line levels?
Using mismatched line levels can result in audio issues like distortion, weak signals, and a poor signal-to-noise ratio. Ensuring that your devices have compatible line-level standards will help maintain optimal audio quality and minimize these problems.
How can I match line levels between devices with different standards?
If you need to connect devices with different line-level standards, you can use attenuators or line-level converters to match the levels. These devices can help bridge the gap between consumer and professional line-level signals, ensuring optimal audio quality in your setup.
Are there any alternatives to using RCA connectors for consumer line-level signals?
Yes, you can use 1/4-inch TS (Tip-Sleeve) connectors as an alternative to RCA connectors for consumer line-level signals. However, keep in mind that TS connectors are unbalanced, meaning they may be more susceptible to noise and interference compared to balanced connections like XLR or TRS.
Conclusion
Well, folks, we’ve reached the end of the line (level)! So did I cover everything you wanted to know? Let me know in the comments section below. I read and reply to every comment. If you found this article helpful, share it with a friend, and check out my full blog for more tips and tricks on this topic. Thanks for reading, and keep those levels in check!
Key takeaways
This article covered linelevel in audio and their connectors. Here are some key takeaways:
- Line level is the standard signal strength used for connecting audio devices and maintaining audio quality.
- There are two main line-level standards: consumer line level (-10 dBV) and professional line level (+4 dBu).
- Different line level connectors include RCA, 1/4-inch TRS, and XLR connectors, each with its specific applications.
- Understanding line-level signals and connectors is essential for setting up your audio gear properly and achieving optimal audio quality.
- Mismatched line levels can lead to audio issues like distortion, weak signals, and a poor signal-to-noise ratio.















