The xylophone, a mesmerizing musical instrument, serves as an intriguing symphony of science and art. It consists of wooden bars arranged like a keyboard, each tuned to a different musical note. When you strike these bars with mallets, they produce a variety of sounds, ranging from bright and clear to warm and resonant. If you’re ready to discover how a simple design can create such a unique range of sounds, and why this instrument is a favorite among musicians and listeners alike, then let’s dive deeper into the mesmerizing world of xylophones.
What is a Xylophone? A xylophone is a musical instrument in the percussion family that consists of wooden bars struck by mallets. Each bar corresponds to a specific pitch, creating a melodic tune when played in succession.
What is a xylophone?
The xylophone is a remarkable instrument in the percussion family. Its name comes from the Greek words “xylon,” which means wood, and “phone,” meaning voice. So, literally, it’s the ‘wooden voice’ – and what a voice it is! This instrument consists of a series of wooden bars that each correspond to a different pitch, just like keys on a piano. And let me tell ya, when you hit those bars with a mallet, magic happens.
Now, don’t get it twisted. Even though I mentioned the analogy with piano keys, a xylophone is quite different. Unlike a piano, the xylophone produces sound through the vibration of the wooden bars when they’re struck. This gives it a unique, clear, and almost bell-like sound that’s hard to miss. Listen to “Rite of Spring” by Stravinsky – there’s a xylophone piece that’ll make your ears perk up, no doubt about it.
AKAI Professional MPK Mini MK3

AKAI Professional MPK Mini MK3
Where did the xylophone come from?
The xylophone is thought to have originated in Southeast Asia and then spread to Africa, where it was modified and adapted by local cultures. The African version, for instance, often had gourd resonators underneath the bars to amplify the sound. Imagine that, making music with gourds and wood – pure organic beats!
Then there’s Europe. The xylophone didn’t really get its time in the limelight there until the 19th century. Yeah, it was fashionably late to the party but showed up with a bang when composers started to feature it in orchestral pieces. From that point on, the xylophone was in. It found a home in the orchestra, and the rest is history.
What are the key components of a xylophone?
A xylophone primarily consists of the following key components:
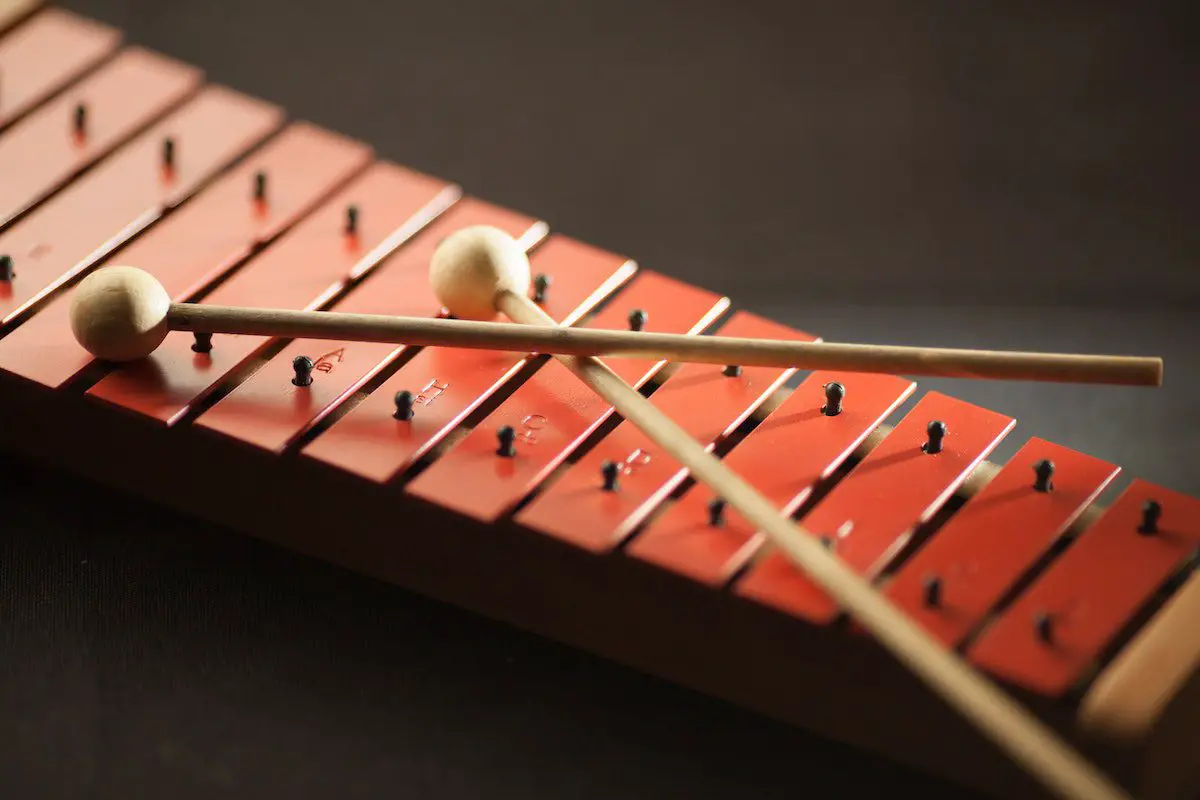
- Bars: The bars are the most crucial part of a xylophone. They are usually made of wood (like rosewood or padouk), and each is carefully tuned to a specific pitch of the musical scale. The bars are arranged similarly to the keys on a piano, with a smaller row of sharp/flat bars located above a larger row of natural bars.
- Resonators: These are tubes or gourds placed below the bars that enhance and amplify the sound produced when a bar is struck. The resonator for each bar is carefully designed to match the pitch of the bar it’s under, allowing it to “resonate” or vibrate sympathetically when the bar is struck, amplifying the sound.
- Frame: This is the structure that holds the bars and resonators in place. It can be made from a variety of materials, but it is usually constructed of wood or metal. The frame needs to be sturdy enough to support the weight of the bars and resonators and withstand the force of the bars being struck.
- Mallets: These are the tools used to strike the bars. Mallets consist of a handle (or shaft), usually made of wood or fiberglass, and a head made of various materials like rubber, plastic, metal, or yarn. As discussed earlier, the hardness and material of the mallet can significantly affect the sound that the xylophone produces.
- Rails: These are horizontal pieces of the frame on which the bars rest. The bars are often suspended on the rails with string or cord, allowing them to vibrate freely when struck.
- End Pieces: These are the vertical parts of the frame at the ends of the rails. They help maintain the xylophone’s structural integrity and stability.
- Accidentals: These are the black keys (sharps and flats) on the xylophone, similar to a piano. They are positioned in a second row, usually above the main row of bars (the naturals).
- Naturals: These are the white keys (natural notes) on the xylophone, similar to a piano. They are positioned in the main row of bars.
Here’s a quick “dos and don’ts” table for playing the xylophone:
| Do’s | Don’ts |
|---|---|
| Do use the right mallets for your instrument and piece. | Don’t strike the bars too hard; you can damage the instrument and create an unpleasant sound. |
| Do aim for the middle of the bars when playing. | Don’t ignore the dynamics in the sheet music; they’re crucial to the piece. |
| Do practice proper grip and technique to prevent injury. | Don’t play without warming up your wrists and hands first. |
| Do listen to a variety of xylophone music for inspiration. | Don’t neglect regular cleaning and maintenance of your instrument. |
What are the different types of xylophones?
Let’s dive into the wonderful world of xylophone varieties. From the concert xylophone that you might see in an orchestra to the African balafon, there’s a xylophone for every beat.
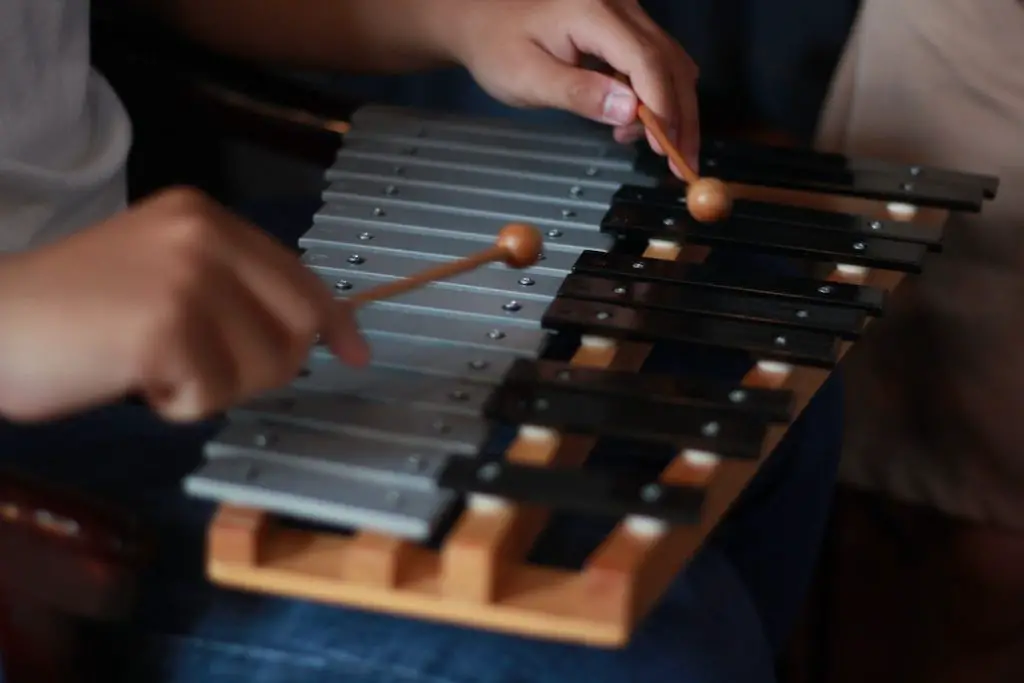

- Concert xylophone: This is tuned to the Western music scale (you know, the ‘do-re-mi’ you learned at school). It typically has a range of three and a half to four octaves, just like your grandma’s old piano. And if you’re in the orchestra scene, you’ve probably got your mallets on one of these.
- Balafon: This is a traditional African xylophone with wooden bars and gourds as resonators. Some of these ancient instruments even have buzzing membranes on the gourds for that extra buzz in your music. Cool, right?
- Marimba: This Central American beauty is like the xylophone’s big cousin. It’s got wider and longer bars that give a deeper and warmer tone, and resonator pipes that amplify the sound. Marimbas are key players (pun intended!) in Latin American music.
- Glockenspiel: The bars are made of steel instead of wood, giving it a bell-like sound. You’ve heard this one in marching bands and sometimes even in rock music. Yep, The Beatles used it in some of their songs!
What’s the role of the xylophone in music?
In the world of classical music, the xylophone has often been the go-to instrument for creating a specific kind of mood or atmosphere. The xylophonist is responsible for adding color, rhythm, and occasionally melody to the overall sound in an orchestra. An example of this is the lively and playful piece by Kabalevsky called “The Comedians.”
Step outside the concert hall, and you’ll find the xylophone taking center stage in traditional music across various cultures, particularly in Africa and parts of Asia.
Step outside the concert hall, and you’ll find the xylophone taking center stage in traditional music across various cultures, particularly in Africa and parts of Asia. It’s not just about the music; the xylophone often carries cultural significance and is a staple at community events and celebrations.
Pop music? Check. Indie folk? You bet. Jazz? Absolutely. The xylophone’s crisp and bright tone has found its way into countless genres, adding an unmistakable sound that can cut through and stand out, or blend seamlessly into the backdrop.
If you want even more tips and insights, watch this video called “Goldon: A Comparison of Xylophones” from the Oskar’s Wooden Ark YouTube channel.
Frequently asked questions (FAQ)
Do you still have questions about xylophones? Below are some of the most commonly asked questions.
How does a xylophone produce sound?
Xylophones produce sound when their wooden bars are struck by a mallet. The vibrations from the struck bar create sound waves, which are then amplified by the resonators underneath. Different bar lengths produce different pitches.
Are xylophones only used in classical music?
Not at all! While xylophones do have a storied history in classical music, they’re incredibly versatile and have found their way into various other genres as well. You’ll hear them in everything from traditional African music to modern pop and indie folk.
What’s the difference between a xylophone and a marimba?
While both instruments are part of the percussion family and use a similar structure of wooden bars and mallets, the main difference lies in their size and sound. A marimba has wider and longer bars, producing a deeper and warmer tone compared to the xylophone’s brighter tone.
Conclusion
Well folks, we’ve certainly struck the right note with this one, haven’t we? Who knew the xylophone could be so diverse and dynamic, from its wooden origins to its place in modern music? It really ‘bar’s none when it comes to versatility. Are there other musical instruments you’d like to learn about? Or perhaps there’s a specific topic related to music production that’s been on your mind? Let me know in the comments below. I read and reply to every comment. If you found this article helpful, share it with a friend, and check out my full blog for more tips and tricks on music production. Thanks for reading and keep those beats rolling!
Key Takeaways
This article covered the multifaceted world of xylophones. Here are some key takeaways:
- A xylophone is a musical instrument in the percussion family that consists of wooden bars struck by mallets. Each bar corresponds to a specific musical note, similar to the keys on a piano.
- The xylophone has its origins in Southeast Asia and Africa and has evolved over the centuries, with variations like the balafon and the marimba originating from different parts of the world.
- In terms of playing the xylophone, it’s all about using the right mallets and striking the bars in the center with the right amount of force.
- The xylophone is incredibly versatile, finding its place in a variety of musical genres, from classical to pop to traditional African music.
- There are various types of xylophones, each with its unique characteristics and sound. These include the concert xylophone, the balafon, the marimba, and the glockenspiel.















