Are you ready to bring some clarity to the murky world of audio production? Well, let’s talk about EQ or equalization! This little tool is a game-changer when it comes to enhancing your audio quality, and I’ve got the inside scoop on everything you need to know.
In this post, we’re going to dive deep into the nitty-gritty of EQ. We’ll cover the basics, including what it is, how it works, and why it’s so essential. We’ll explore the different types of EQ and which ones are best suited to your needs. Whether you’re a seasoned pro or just starting in the audio world, you’re going to want to read this.
What is EQ in audio? EQ (Equalization) is a tool used in audio processing to adjust the balance between frequencies. It allows for enhancing or reducing specific elements in a recording, resulting in a cleaner, more balanced sound.
What is EQ in music?
EQ in music stands for equalization, which is the process of adjusting the balance of different frequency components in an audio signal. Every note an instrument plays has a fundamental frequency and overtones above it, which give it a specific timbre and make it recognizable. EQ is the tool used to manipulate the frequency content of a mix to ensure all the elements of production work together sonically.

Musicians use EQ to improve the overall quality of their mix by making room for different elements in the frequency spectrum…
EQ allows you to adjust the volume level of a frequency or range of frequencies within a sound or audio signal, thereby allowing you to cure a sound or entire song of its imperfections and accentuate its good sides. EQ components include filters that help to cut unwanted frequencies and boost necessary ones to achieve balance and clarity in the mix.
In music production, the EQ is one of the most used tools in the mixing toolbox. Musicians use EQ to improve the overall quality of their mix by making room for different elements in the frequency spectrum, ensuring that each element has its own space and is heard clearly. Knowing how to use EQ in music is essential to achieve a professional-sounding mix.
AKAI Professional MPK Mini MK3

AKAI Professional MPK Mini MK3
How does EQ work?
EQ works by boosting or cutting the volume level of specific frequencies or frequency ranges in an audio signal. EQ processors typically feature a number of frequency bands or sections, each of which corresponds to a range of frequencies. These frequency sections allow the user to adjust the volume level of specific frequency ranges in the audio signal.
EQ can be applied to a variety of audio sources, such as vocals, instruments, and mix buses. For instance, in the case of vocals, EQ can be used to attenuate or boost frequencies that affect the clarity or warmth of the singer’s voice. Similarly, in the case of instruments, EQ can be used to enhance specific frequencies to bring out the natural character of the instrument or to remove unwanted frequencies that may cause muddiness in the mix.
What are the types of EQ?
There are several types of EQ in music production and audio engineering. Here are some of the most common ones:
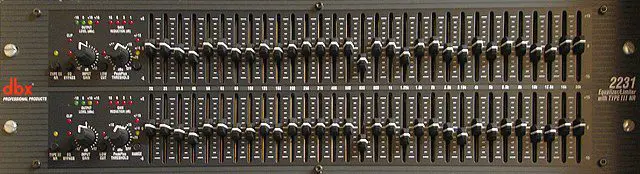
1. Graphic EQ
Graphic EQ is a type of EQ that features a series of sliders or faders that correspond to specific frequency bands. Graphic EQs are often used for live sound applications and are useful for making broad adjustments to the frequency content of an audio signal.
2. Parametric EQ
Parametric EQ is a type of EQ that allows the user to adjust specific frequency ranges with greater precision than a graphic EQ. Parametric EQs typically feature frequency controls for adjusting the center frequency, bandwidth, and gain.
3. Shelving EQ
Shelving EQ is a type of EQ that boosts or cuts frequencies above or below a specific cutoff point. Shelving EQs are useful for making broad adjustments to the frequency content of an audio signal.
4. High-pass and low-pass filters
High-pass and low-pass filters are types of EQ that attenuate or cut frequencies above or below a specific cutoff point. High-pass filters are useful for removing low-frequency rumble or noise, while low-pass filters can be used to remove high-frequency noise or hiss.
5. Dynamic EQ
Dynamic EQ is a type of EQ that applies compression or expansion to specific frequency ranges based on the level of the audio signal. Dynamic EQs are useful for controlling harsh frequencies or resonances in an audio signal.
When and how do you use EQ in mixing?
EQ is an essential tool in mixing as it allows you to balance and shape the frequency content of individual tracks and the overall mix. Here are some tips on when and how to use EQ in mixing:
1. Start with EQ subtractively
Before adding any EQ, listen to the track and identify problem areas such as resonances, harsh frequencies, or muddiness. Use EQ subtractively to remove or cut those problem frequencies. This helps to make space in the mix for other elements to sit better.
2. Use EQ to make each track sit in its own frequency range
Use EQ to carve out specific frequency ranges for each track in the mix. For example, use EQ to boost the low end of the bass guitar and cut the low end of the kick drum to avoid clashes between the two. Similarly, use EQ to cut the low mids of the guitar to make space for the vocals.
3. Be subtle with EQ adjustments
Avoid making drastic EQ adjustments, as this can result in unnatural or phasey sounds. Instead, make small and subtle EQ adjustments until you achieve the desired result.
4. Use EQ creatively
EQ can also be used creatively to add character and warmth to a track. For example, boosting the high-end of a guitar can add sparkle and presence to the track, while boosting the mid-range of a vocal can add warmth and intimacy.
5. Use EQ in conjunction with other processing tools
Finally, use EQ in conjunction with other processing tools, such as compression and reverb, to achieve a balanced and professional-sounding mix.
What are some tips for using EQ?
Here are some tips for using EQ effectively:
1. Start with the good source material
Good source material is the foundation of a great mix. Make sure the tracks you’re working with are well-recorded and well-performed.
2. Use EQ subtractively
Start by cutting or attenuating frequencies that are causing problems instead of boosting frequencies to make a track sound better. This will help to make space in the mix for other elements to sit better.
3. Be subtle with EQ adjustments
Avoid making drastic EQ adjustments, as this can result in unnatural or phasey sounds. Instead, make small and subtle EQ adjustments until you achieve the desired result.
4. Use EQ in context
Listen to the track in the context of the mix when making EQ adjustments. This will help you to make informed decisions about how to shape the frequency content of the track to fit within the overall mix.
5. Use EQ creatively
EQ can also be used creatively to add character and warmth to a track. For example, boosting the high-end of a guitar can add sparkle and presence to the track, while boosting the mid-range of a vocal can add warmth and intimacy.
6. Use mid-side EQ for stereo tracks
Mid-side EQ is a technique used to adjust the levels of the center and sides of a stereo track separately. This can be useful for making adjustments to the stereo image of the track.
7. Use EQ sparingly
Be careful not to over-equalize a track, as this can result in an unnatural or phasey sound. Use EQ sparingly and only when necessary.
8. Use narrow Q settings to locate problematic frequencies
When looking for problematic frequencies, set the Q to a narrow setting, boost the gain by 7-10 dB, and sweep the frequency range until you locate the frequency that is causing the problem.
Conclusion
Well, that’s it, folks! We’ve covered everything you need to know about EQ in audio production. From the basics of balancing frequencies to the ins and outs of EQ plugins, we’ve explored all the important aspects of this powerful tool.
Did I cover everything you wanted to know? Let me know in the comments section below (I read and reply to every comment). If you found this article helpful, share it with a friend, and check out my full blog for more tips and tricks on audio production. As always, thanks for tuning in, and keep those frequencies in check!
Key takeaways
This article covered EQ (equalization). Here are some key takeaways:
- EQ (Equalization) is an essential tool in audio production for adjusting the balance between frequencies.
- It allows for enhancing or reducing specific elements in a recording, resulting in a cleaner, more balanced sound.
- EQ works by boosting or cutting specific frequency ranges to improve the presence of particular elements in a recording.
- There are different types of EQ, including parametric, graphic, and shelving EQ.
- Basic EQ techniques for beginners include cutting vs. boosting frequencies and creating space for individual instruments.
- Choosing the right EQ plugin is essential for achieving the desired sound quality.















