The concept of a Fourier transform may sound like a complicated concept, but it doesn’t have to be. In this post, we’ll dive into the world of Fourier Transform in audio. So sit back, relax, and let’s get ready to transform the way you think about audio.
What is Fourier Transform (FT)? Fourier Transform in audio is a mathematical technique used to analyze and manipulate audio signals. It works by breaking down a complex waveform into its individual frequency components, allowing for the identification and removal of unwanted noise or distortion. The concept of Fourier Transformation is an essential tool for audio engineers, musicians, and anyone interested in the science of sound.
How does Fourier transform work?
Fourier Transform (FT) is used to analyze the frequencies present in a sound wave. Sound waves are composed of a combination of various frequencies, and the FT can separate these frequencies into their individual components.
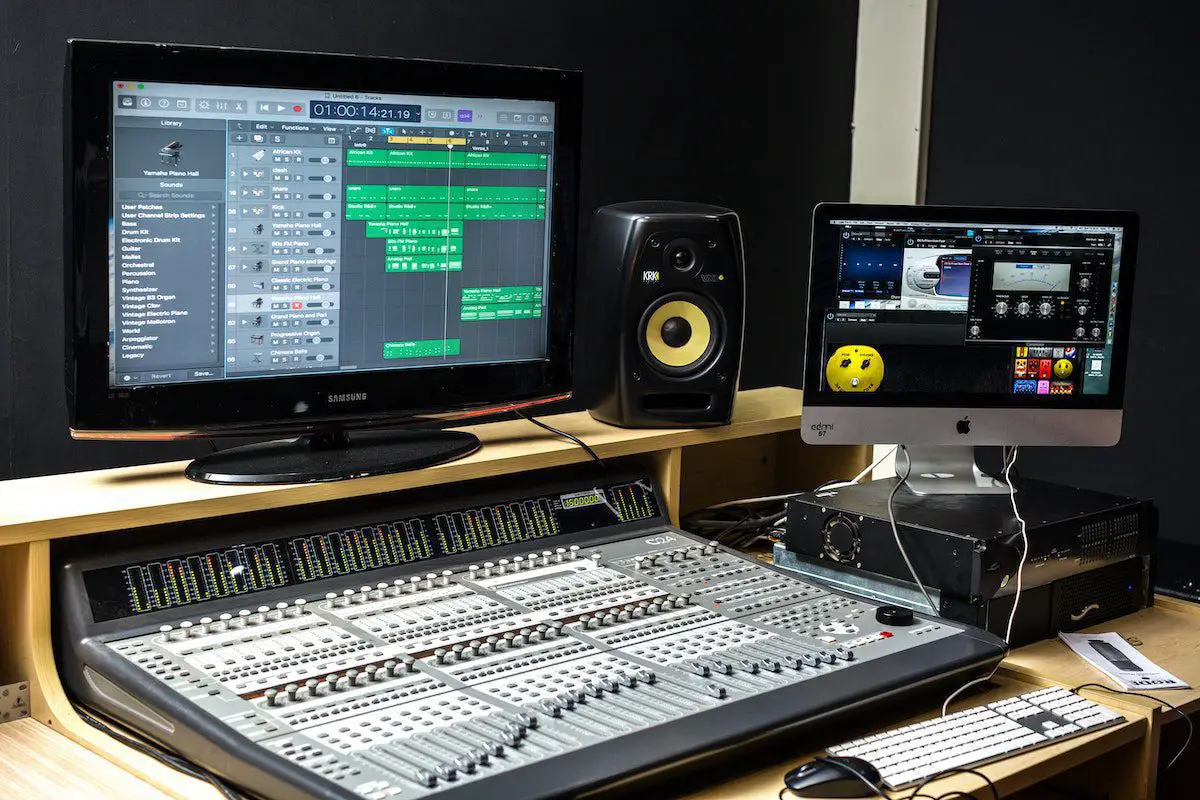

When a sound wave is recorded, it is first sampled at a specific rate, usually referred to as the sampling rate. The samples are then converted into a digital signal, which can be analyzed using FT. The FT can be used to convert the digital signal from the time domain to the frequency domain, which allows us to see which frequencies are present in the signal and how strong they are.
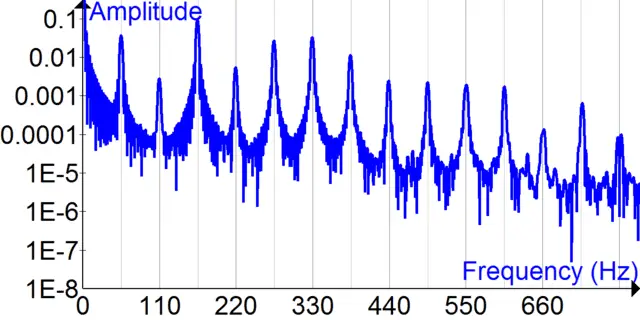
This powerful conversion technique enables us to recognize the various frequencies present within a signal. To illustrate, one can apply the Fourier transform to an audio signal to identify different sounds or tones it contains.
AKAI Professional MPK Mini MK3

AKAI Professional MPK Mini MK3
What are the applications of Fourier transform in audio?
The FT is used to analyze the pitch and timbre of musical notes. By analyzing the frequency components of a musical note, it is possible to determine its pitch and other properties. This information is used in many applications, such as music transcription, automatic chord recognition, and musical instrument identification.
Other uses of FT
The FT may also be used to measure the acoustic properties of a space or a device. By analyzing the frequency response of a room or a loudspeaker, it is possible to determine its resonant frequencies, frequency response, and other properties. This information is used in many applications, such as room acoustics design, loudspeaker design, and acoustic measurements in the automotive and aerospace industries.
Conclusion
And there you have it, folks, Fourier Transform in audio broken down into bite-sized pieces. Now, don’t worry if you’re still feeling a bit perplexed – this stuff isn’t exactly easy to wrap your head around. But hopefully, this post has given you a foundation to build upon.
Did I cover everything you wanted to know? Let me know in the comments section below (I read and reply to every comment). And hey, if you found this article helpful, share it with a friend who’s also interested in audio.
Key takeaways
This article covered Fourier Transform in audio. Here are some key takeaways:
- Fourier Transform in audio is a mathematical technique for analyzing and manipulating audio signals.
- It breaks down a complex waveform into its individual frequency components, enabling the identification and removal of unwanted noise or distortion.
- Understanding Fourier Transform is essential for audio engineers, musicians, and anyone interested in the science of sound.
















You need to fix this page! I lost all hundreds of characters of text probably because of that ridiculous restriction against pasting.