When it comes to audio equipment, one critical player is ‘Frequency Response.’ When tuning into your favorite song on a new set of speakers, headphones, or sound system, the rich bass notes, the crisp high tones, and everything in between are shaped and defined by frequency response. But what exactly is a frequency response, and how does it shape your listening experience? Let’s unravel this sonic mystery together, shall we?
What is frequency response? Frequency response refers to the ability of an audio component to accurately reproduce the full range of audible sound frequencies, from the low bass to the high treble. It determines how faithfully a device can reproduce different pitches and impacts the overall tonal balance and clarity of your music.
What is frequency response?
Frequency response is a visual representation of how well an audio component reproduces the audible range of sound. It essentially shows how well a device can handle different pitches of sound. Imagine a graph with two axes. On the horizontal x-axis, we have frequency, which represents the pitch of the sound in Hertz (Hz). On the vertical y-axis, we have amplitude, which shows us the loudness of the sound in decibels (dB).
By plotting these two values, we can create a frequency response graph. Ideally, we want to see a nice, straight line across the graph—this is what we call a “flat” frequency response. It means that the audio component reproduces all frequencies equally, without favoring any particular range. So, the output matches the input, giving you an accurate representation of the original sound.
However, things aren’t always that simple. In reality, you’ll often see peaks and dips in the frequency response graph. These variations can indicate that the audio component emphasizes or attenuates certain frequencies. For example, a peak around the bass frequencies might give you that extra thump, while a dip in the midrange might make the vocals sound less prominent.
AKAI Professional MPK Mini MK3

AKAI Professional MPK Mini MK3
Why does frequency response matter?
Well, it directly affects the way your music sounds. An accurate and balanced frequency response ensures that you’re hearing the music as the artists and engineers intended. It preserves the integrity of the mix, ensuring that no instrument or frequency range is unfairly emphasized or masked.
By choosing audio components with accurate and reliable frequency response, such as studio monitors or headphones, you’ll have a solid foundation during the mixing and mastering process. Remember, a clear and faithful frequency response is like having a trustworthy set of ears in your studio.
What affects the frequency response of audio components?
When it comes to audio components like headphone drivers and speakers, a variety of factors can contribute to non-linearity and affect frequency response. Mechanical properties, such as the materials used and the design of the drivers, can introduce variations. Electronics, including impedance matching between amplifiers and crossover components, also play a role. Even the acoustics of the room you’re in can impact the final frequency response you hear.
What does frequency range variation mean for our listening experience?
In our pursuit of flat response, we often come across specifications that provide a frequency range with a variation quoted in decibels. For example, 20Hz-20kHz +/- 6 dB. This variation tells us the maximum deviation at any point within the given range.
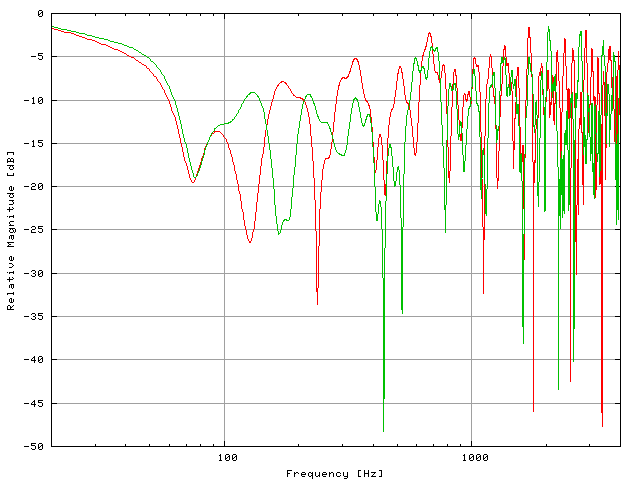
Smaller deviations of 1 or 2 dB may not be cause for concern, as they are often not perceivable. However, deviations of 3 dB or more can start to affect our listening experience. Resonant frequencies, in particular, can create pronounced bumps on the frequency response graph, exaggerating certain notes or masking others.
When assessing frequency response, it’s not just about the overall range and deviations; it’s also about the smoothness of the response curve. A highly variable frequency response can introduce unwanted coloration or tonal imbalances to the sound. On the other hand, a smoother frequency response, with minimal fluctuations, is considered more desirable and closer to the ideal of a flat response.
To help you navigate the challenges of obtaining a flatter frequency response, here are some dos and don’ts to keep in mind:
| Dos | Don’ts |
|---|---|
| Do choose audio components with accurate frequency response. | Don’t rely solely on frequency range specifications. |
| Do consider the mechanical and acoustic properties of your listening environment. | Don’t ignore the impact of resonance on the sound. |
| Do aim for a smooth and consistent frequency response curve. | Don’t obsess over small deviations within acceptable limits. |
What is Fourier analysis?
When we listen to music, we hear a wide variety of sounds produced by different instruments. But did you know that these sounds can be broken down into simpler components called sine waves? Fourier analysis tells us that complex waveforms can be expressed as a sum of sine waves with varying amplitudes. This is where the magic happens!
How do harmonics affect the sound?
Harmonics are the key to understanding the unique qualities of different instruments. They are the additional frequencies that accompany the fundamental frequency of a sound, creating a rich and colorful texture. For example, when you play a natural C on the violin, you not only hear the fundamental frequency of 261 Hz but also harmonics at multiples of that frequency (522 Hz, 783 Hz, 1044 Hz, and so on).
Different instruments have different harmonic content, which contributes to their unique timbre and tonal qualities. For example, a piano and a violin playing the same note will have different harmonic profiles. Understanding the harmonic content of each instrument helps us appreciate their individuality and ensures accurate reproduction in our audio systems.
What is the impact of non-flat frequency response on harmonics?
Now, here’s the catch. Remember when we talked about non-flat frequency response? Well, it turns out that variations in frequency response can affect the harmonic content of the sound. If certain frequencies are emphasized or attenuated, it can alter the way instruments sound in the mix.
To create well-balanced and professional mixes, it’s important to consider the harmonic content of each instrument…
This means that a non-linear frequency response not only affects the overall tonal balance but also impacts the perception of individual instruments. To create well-balanced and professional mixes, it’s important to consider the harmonic content of each instrument and how it interacts with frequency response.
By carefully sculpting the frequency response and ensuring accuracy across the audio chain, you can maintain the integrity of the harmonics and preserve the true character of each instrument. This allows you to create a sonic landscape where every instrument shines and blends harmoniously.
If you want even more great tips and information, check out the video below.
Frequently asked questions (FAQ)
As we wrap up this blog post on frequency response, let’s address some common questions that may still be lingering in your mind.
How does frequency response impact the sound quality of my recordings?
The frequency response of your audio equipment influences how accurately it reproduces different frequencies, which directly affects the tonal balance and clarity of your recordings. A flat frequency response ensures faithful sound reproduction, whereas deviations can introduce coloration and inaccuracies.
Can I improve the frequency response of my headphones or speakers?
While you can’t fundamentally change the frequency response of your headphones or speakers, you can make adjustments using equalization (EQ). EQ allows you to boost or attenuate specific frequencies to achieve a more desirable balance or compensate for any deviations in the frequency response.
How can I measure the frequency response of my audio equipment?
To measure the frequency response, you can use specialized audio measurement tools like audio analyzers or software applications that generate test signals and analyze the output. These tools provide visual representations of the frequency response, helping you identify any variations or anomalies.
Conclusion
In the wild world of frequency response, it’s crucial to understand how it impacts the quality and fidelity of our music productions. By grasping the concept of frequency response and its relation to harmonics, we can unlock the true potential of our audio creations. Remember, a flat frequency response is the key to faithful sound reproduction and accurate mixing decisions.
So, did I cover everything you wanted to know? Let me know in the comments section below (I read and reply to every comment). If you found this article helpful, share it with a friend, and check out my full blog for more tips and tricks on frequency response. Thanks for reading and keep grooving to the beat of great sound!
Key Takeaways
- Frequency response represents how accurately an audio component reproduces different frequencies.
- Harmonics play a vital role in shaping the unique sound characteristics of instruments.
- Non-flat frequency response can affect the tonal balance and perception of individual instruments.
- Understanding and managing frequency response is essential for creating well-balanced mixes and accurate sound reproduction.















