Have you ever wondered what lies beyond the realm of audible sound? Step into the world of ultrasonic sound, where frequencies defy the limits of our ears and open up a whole new dimension. From medical imaging to the secret language of bats and dolphins, explore the hidden power of ultrasonic waves and embark on a journey that transcends the boundaries of our hearing.
What is ultrasonic sound? Ultrasonic sound refers to frequencies that surpass the range of audible sound, captivating us with its unseen power and finding applications in various fields, including medical imaging and communication among certain species.
How is ultrasonic sound used by animals?
Ultrasonic sound finds fascinating applications in the realms of communication and navigation, captivating the animal kingdom and pushing the boundaries of our understanding. So, how do creatures like bats and dolphins utilize this invisible power?
Bats: A sonar symphony
Bats have long been hailed as the nocturnal masters of navigation, maneuvering through pitch-black darkness with astonishing precision. They achieve this through a remarkable phenomenon called echolocation. By emitting ultrasonic sounds and listening to the echoes bouncing back, bats can build a detailed auditory map of their surroundings.
These tiny creatures use ultrasonic frequencies in the range of 20-100kHz, which allows them to detect objects, obstacles, and even prey. As they fly, they continuously emit ultrasonic chirps, interpreting the echoes that return to their ears. Imagine a bat navigating through a crowded forest, deftly dodging branches and capturing insects mid-flight with the help of its ultrasonic sonar system—a true marvel of nature!
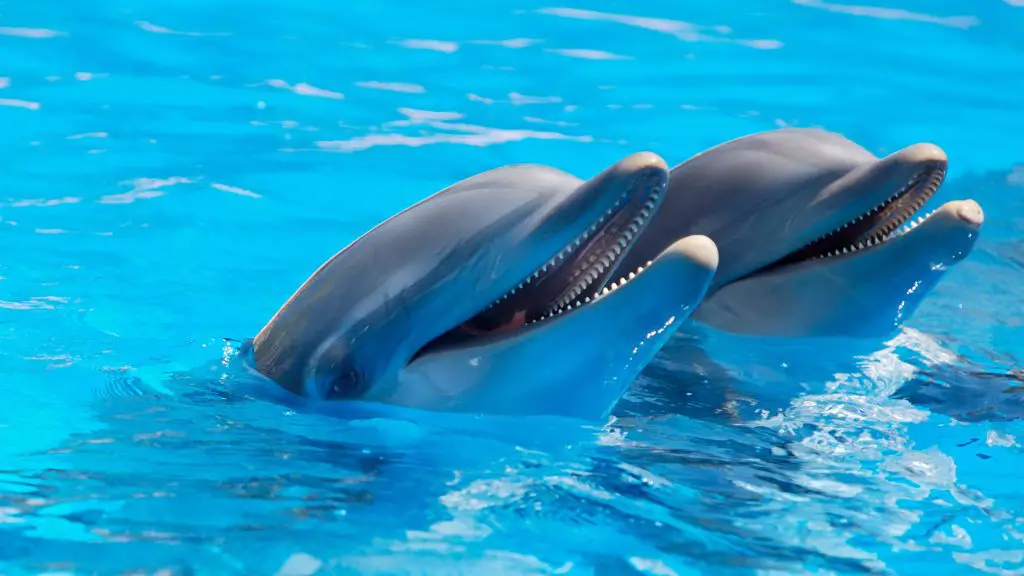
Dolphins: Clicks and communication
Dolphins, those charismatic ocean dwellers, have their own ultrasonic symphony playing beneath the waves. They are known for their sophisticated communication skills and exquisite use of echolocation. Similar to bats, dolphins emit ultrasonic clicks but with an even broader frequency range.
These intelligent marine mammals primarily use ultrasonic clicks in the range of 20-100kHz for communication, navigation, and hunting. The clicks are produced in their nasal passages and focused through the melon, a structure on their forehead.
As the clicks travel through the water, they encounter objects and bounce back as echoes. Dolphins then interpret these echoes, allowing them to navigate, locate prey, and communicate with one another.

AKAI Professional MPK Mini MK3

AKAI Professional MPK Mini MK3
How are ultrasonic sounds used in medical applications?
In the world of medical ultrasound, ultrasonic sounds are produced using specialized devices called ultrasonic transducers. These transducers consist of piezoelectric crystals that convert electrical energy into ultrasonic waves. When an electric current is applied to the crystals, they vibrate, emitting ultrasonic waves at the desired frequency.
The applications of ultrasonic sound in the field of medicine are truly remarkable. Ultrasonic waves, with their ability to penetrate soft tissues, have become a valuable tool for non-invasive diagnostic imaging. Let’s explore a few of the key medical applications:
Echocardiogram
Echocardiography, commonly known as an echocardiogram, captures the moving image of the heart’s action using ultrasonic waves. This powerful diagnostic technique allows healthcare professionals to assess the structure and function of the heart, detect abnormalities, and evaluate blood flow. By employing false colors to indicate the speed and direction of blood flow and heart valve movements, an echocardiogram provides crucial insights into cardiac health.
Whether it’s assessing organs, monitoring pregnancies, or detecting tumors, ultrasonic waves serve as a non-invasive and safe method for diagnostic imaging.
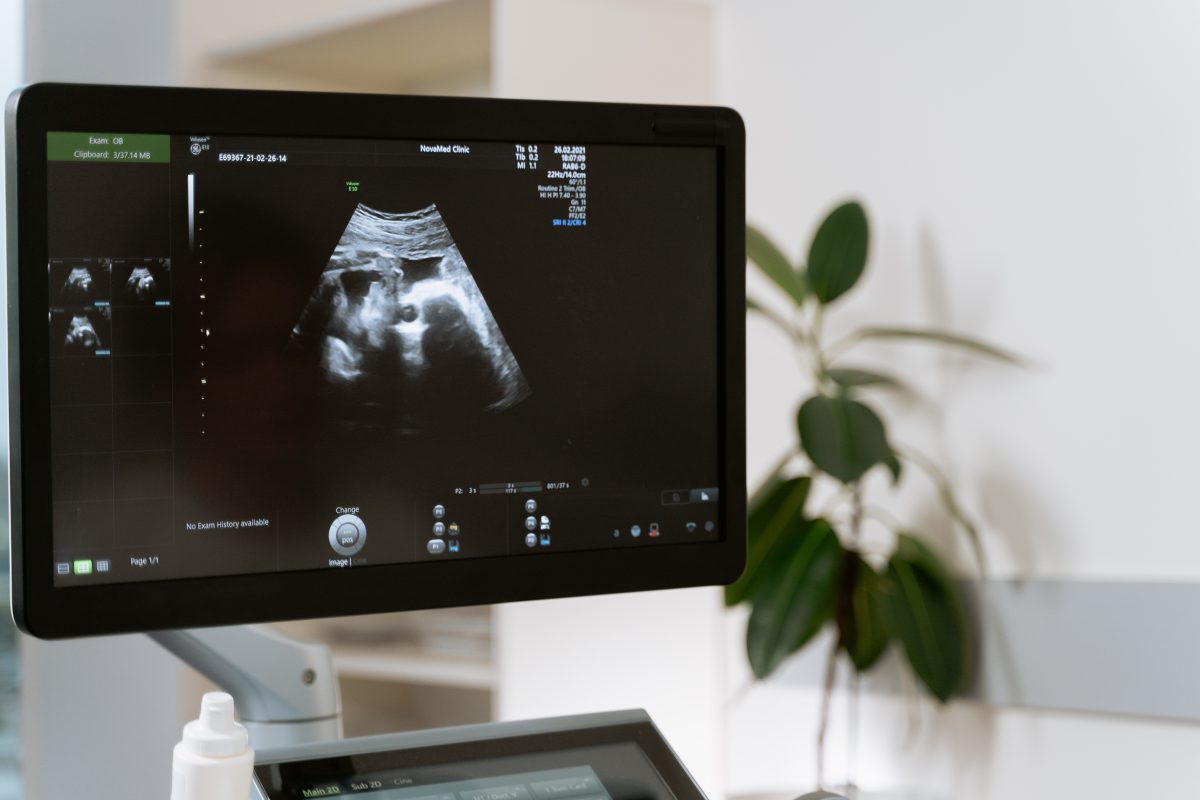
Ultrasonic imaging
Ultrasound imaging has revolutionized the way we visualize the internal structures of the human body. Whether it’s assessing organs, monitoring pregnancies, or detecting tumors, ultrasonic waves serve as a non-invasive and safe method for diagnostic imaging. With resolutions capable of capturing details less than a millimeter near the body’s surface, ultrasound imaging provides invaluable information to guide medical interventions.
The resolution of ultrasound imaging decreases with the depth of penetration due to the need for lower frequencies, as higher frequencies are attenuated more by tissue.
Ultrasonic frequencies across various animals and technologies
The following table provides a comparison of various animals and technologies known to emit, receive or utilize ultrasonic sound. Ultrasonic sound refers to sound frequencies above 20,000 Hz, which is typically the upper limit of human hearing. Different animals and technologies use these high-frequency sounds for various purposes, such as navigation, communication, or detection.
| Species/Technology | Purpose of Ultrasonic Use | Frequency Range (kHz) |
|---|---|---|
| Human (technology) | Ultrasound Imaging | 2,000-18,000 |
| Bat | Echolocation | 20-200 |
| Dolphin | Echolocation | 75-150 |
| Dog | Hearing | 40-60 |
| Mouse | Communication | 30-90 |
| Moth | Defense against predators | 20-60 |
| Rat | Communication | 20-100 |
| Ultrasonic Cleaner | Cleaning surfaces | 20-400 |
| Ultrasonic Sensor | Distance measuring | 40-400 |
Advantages and disadvantages of ultrasonic sound
Ultrasonic sound has proven to be a powerful tool in various fields, including medical diagnostics and communication. However, like any technology, it comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Let’s explore both sides of the coin!
Advantages of ultrasonic sound
- Non-invasive imaging: Ultrasonic waves enable non-invasive imaging, allowing healthcare professionals to visualize internal structures without the need for invasive procedures.
- Safe and radiation-free: Unlike other imaging techniques like X-rays, ultrasonic sound is safe and does not involve harmful ionizing radiation, making it suitable for repeated examinations and monitoring.
- Real-time imaging: Ultrasonic imaging provides real-time visual feedback, allowing for immediate interpretation and on-the-spot adjustments during medical procedures.
- Portable and accessible: Ultrasonic devices have become increasingly portable and accessible, making them valuable tools in remote areas or emergency situations where immediate diagnostic insights are crucial.
Disadvantages of ultrasonic sound
- Limited penetration: Ultrasonic waves have limited penetration capabilities, as they are absorbed and attenuated by certain tissues and bones, making it challenging to visualize deep structures.
- Lower resolution at depth: As we venture deeper into the body, lower-frequency ultrasonic waves must be used, resulting in lower resolution and reduced ability to capture fine details.
- Operator dependency: Ultrasonic imaging heavily relies on the operator’s skill and experience, as obtaining high-quality images requires proper positioning, angling, and interpretation.
- Limited availability of specialized expertise: Interpreting ultrasonic images and performing complex procedures may require specialized expertise, limiting access in certain regions or healthcare settings.
While ultrasonic sound offers numerous advantages in medical diagnostics and beyond, it’s important to consider its limitations and the expertise required for optimal utilization. By weighing the pros and cons, healthcare professionals can make informed decisions and provide the best possible care for patients.
If you want even more great tips and information, watch this video called “How Does Ultrasound Work?” from the NIBIB gov YouTube channel.
Frequently asked questions (FAQ)
Do you still have questions about ultrasonic sound? Below are some of the most commonly asked questions.
How safe is ultrasonic imaging?
Ultrasonic imaging is considered safe and non-invasive. Unlike X-rays, it does not involve ionizing radiation. It is widely used in medical diagnostics, and precautions are taken to ensure patient safety, such as using appropriate frequencies and avoiding prolonged exposure.
Can ultrasonic sound harm human hearing?
Ultrasonic sound above the range of audible frequencies (20,000 Hz) is generally not harmful to human hearing. However, it’s important to avoid prolonged exposure to extremely high levels of ultrasonic sound, as it may cause discomfort or potential damage to hearing.
Are there any risks associated with ultrasonic imaging during pregnancy?
Ultrasonic imaging has been used in prenatal care for many years without evidence of harmful effects on the fetus. However, it’s recommended to adhere to the guidelines and limit exposure to medically necessary examinations.
Conclusion
And there you have it. The fascinating world of ultrasonic sound has been unveiled! From its applications in medical diagnostics to the intriguing communication methods of bats and dolphins, ultrasonic waves have proven to be a powerful tool. So, the next time you hear someone mention ultrasonic sound, remember that it’s more than just a high-pitched tune—it’s a symphony of knowledge and discovery!
Just remember, if you ever find yourself in a soundproof room, don’t worry; you’re not alone. It’s just the sound waves having a quiet party without you!
And did I cover everything you wanted to know? Let me know in the comments section below (I read and reply to every comment). If you found this article helpful, share it with a friend, and check out my full blog for more tips and tricks on everything about audio. Thanks for reading, and keep groovin’!
Key takeaways
This article covered the topic of ultrasonic sound and its applications. Here are some key takeaways:
- Ultrasonic sound refers to frequencies above the range of audible sound.
- Bats and dolphins utilize ultrasonic sound for communication and navigation.
- Ultrasonic waves are produced using specialized transducers in medical imaging.
- Medical applications include echocardiograms and non-invasive ultrasound imaging.
- There are limitations in resolution with increased depth and the inverse relationship between wavelength and maximum resolution.















